Discover the impact of case management on the healthcare system with our comprehensive new fact sheet. Designed specifically for healthcare professionals, this resource delves into how case management enhances patient outcomes, reduces costs, and more. Download the fact sheet today to gain valuable insights for leveraging case management.


The Impact of Case Management on the Healthcare System
Introduction to Case Management
Factors impacting the current healthcare landscape, such as the rise in the aging population, chronic conditions, and costs, have strained the healthcare system. As a result, healthcare stakeholders are moving toward value-based care, emphasizing quality and outcomes rather than the volume of services provided.1 The demand for specialized health professionals capable of supporting individuals and their caregivers as they navigate increasingly complex and fragmented healthcare settings has increased.2
Case management has become essential in improving the management of complex physical, psychological, and/or social determinants of health.2 It supports the goals of value-based care by promoting cost-effective strategies that support better quality, improved outcomes, and higher consumer satisfaction. Case management serves to achieve consumer wellness and autonomy through advocacy, communication, education, identification of service resources, and service facilitation.3
What Is Case Management?
Case management has become essential in improving the management of complex physical, psychological, and/or social determinants of health. It supports the goals of value-based care by promoting cost-effective strategies that support better quality, improved outcomes, and higher consumer satisfaction. Case management serves to achieve consumer wellness and autonomy through advocacy, communication, education, identification of service resources, and service facilitation.4
Who Are Professional
Case Managers?
Case managers are healthcare professionals who serve as patient advocates, supporting, guiding, and coordinating care for patients, families, and caregivers as they navigate their health and wellness journeys. They serve as the center of communication, connecting individuals/caregivers with members of the healthcare team and community to impact acute and chronic disease management and improve population health.2
"Well-deserved and long-overdue recognition for the important work of case managers. Case managers connect systems and services for our most vulnerable patients. They are crucial members of health care teams striving for high-quality, person-centered care across all providers and settings."
- Gerri Lamb, PhD, RN, FAAN
Professor Emerita, Arizona State University
About Case Management Practice
Case managers support an evidence-based approach to assist patients/clients in achieving their healthcare goals. These efforts promote better clinical and financial outcomes for individual patients/clients and the population. Effective case management positively impacts the healthcare system, especially in aligning with the goals of the Quintuple Aim, which includes improving health outcomes of individuals/populations, enhancing the experience of care, reducing the costs of care, improving the care team experience, and addressing social determinants of health/health equity.4,5

Guiding Principles Followed by Case Managers
Case management is grounded in professional practice and advocacy. The case manager applies guiding principles into practice based on the individual needs and preferences in collaboration with the interprofessional healthcare team to deliver care and services that are safe, appropriate, effective, person-centered, timely, efficient, and equitable.4
Populations Served by Case Managers
Case managers support individuals and populations across the human lifespan from birth to end-of-life. They assist patients/clients and their caregivers in navigating the healthcare system working with high-risk populations including but not limited to maternal, pediatric, complex medical and psychosocial, chronic condition, oncology, disabled, traumatic injuries, homeless, substance use disorder, mental health, geriatric, and palliative/hospice populations.
Case Management Practice Settings
Professional case management practice spans all healthcare settings across the continuum of care. The following practice settings include:4
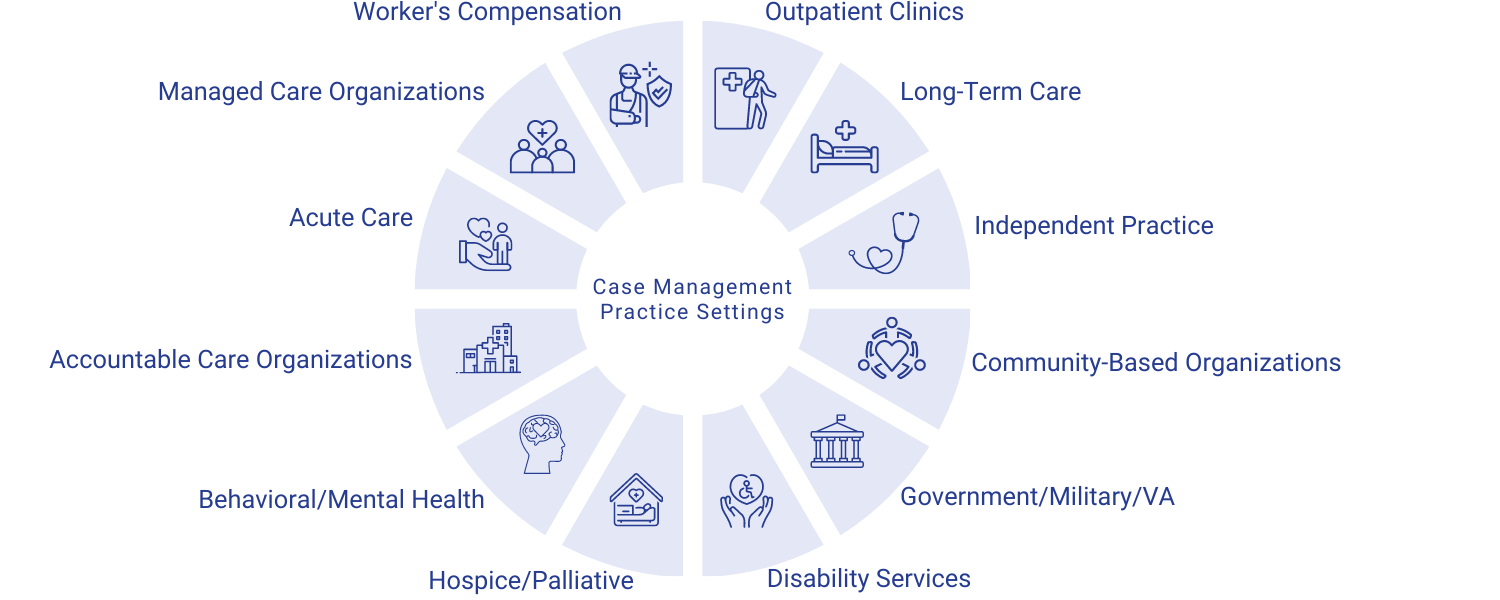
Services Provided by Case Managers
Case managers are vital in coordinating care and services for individuals with various complex needs.6 Core components of the case management process are carried out to assist individuals in achieving optimal health outcomes, which include client identification, engagement, assessment, development of a person-centered care plan with prioritized goals, implementation of the care plan, monitoring and evaluation, and closure of case management services.4
Case managers tailor interventions to meet the needs and preferences of the individuals/ populations they serve and contribute to the goals of population health management. Collectively, case management interventions enhance patient/client safety, well-being, and quality of life.4
The case manager has evolved into an essential and invaluable member of the healthcare team, with their central focus being care activities supporting the patient. The care manager provides comprehensive oversight over the patient care process while serving first and foremost as a patient and family advocate.
- Alpesh N. Amin, MD, MBA, MACP, MHM, FRCP, FACC, FHFSA, CPE
Associate Dean for Clinical Transformation
Professor & Chair Department of Medicine
Chief & Executive Director, Hospital Medicine
University of California, Irvine Health
Factors That Support Demand for Case Managers
Several factors support the increased demand for professional case management services, such as the rise in the aging population, chronic conditions, substance use disorder, mental health, disability, and complex medical and psychosocial needs population that benefits the most from case management services.
1. Aging Population
Worldwide, the population of people 65 and over will double to 1.6 billion by 2050.5 Aging increases the risk of chronic diseases such as dementia, heart disease, type 2 diabetes, arthritis, and cancer. These are the nation’s leading drivers of illness, disability, death, and health care costs. The risk of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias increases with age, and these conditions are most common in adults 65 and older.8
2. Frequent Users of Healthcare Services
Frequent users of health care services account for approximately 10% of the population but upward of 70% of health care expenditures. Frequent users have chronic physical diseases that are further complicated by mental health comorbidities and/or social vulnerabilities, which increase their overall healthcare needs.13
3.Chronic Conditions
Chronic diseases are the leading causes of illness, disability, and death in the United States and the leading drivers of our nation’s $4.1 trillion annual healthcare costs.9 Patients living with chronic illness incur four times more in medical costs, with half over 65 years old spending twice as much out of pocket on healthcare and being three times more likely to be hospitalized.10 In 2019-2020, 20% of adults were experiencing a mental illness. That is equivalent to over 50 million Americans.11
4. Social Determinants of Health/Health Related Social Needs/Health Equity
As high as eighty percent (80%) of an individual’s health is influenced by the non-clinical factors heavily associated with the Social Determinants of Health. Over fifty percent (50%) of hospital readmissions are due to the social determinants of health.10
Health inequities cost the United States roughly $83 billion, which is anticipated to grow to $300 billion by the year 2050.14
5. Healthcare Expenditures
90% of the nation’s $4.1 trillion per year in healthcare expenditures are for people with chronic and mental health conditions.12
The Positive Impact of Case Management on the Healthcare System
Case management interventions focus on improving care coordination and transitions, reducing fragmentation of services, and enhancing safety, well-being, and quality of life. It is a cost-effective strategy for coordinating chronic illness care.4
The underlying premise of case management is based on the fact that when an individual reaches the optimum level of wellness and functional capability, everyone benefits: the individual patient/client being served, the patient/client’s family or caregiver, the reimbursement source or payor, and other involved parties such as employer and healthcare advocates.4
Findings from Research
| Key Indicators | Positive Impact of Case Management |
| Health Outcomes
|
Case management has proven effective in the treatment of many chronic diseases, such as diabetes, hypertension, obstructive pulmonary disease, and cancer care.15 Care management is associated with fewer psychiatric symptoms and greater QOL for persons with serious mental illness.16 |
| Cost Reductions
|
Case management interventions favorably affect healthcare utilization outcomes in chronic illness care. Case management demonstrated reduced utilization: fewer hospital readmissions, fewer ED visits, fewer institutionalization, and reduced costs.17 |
| Frequent Users of Healthcare Services | Case management is a promising intervention for frequent users of healthcare services.18 It is an effective means of reducing frequent users' recurrent ED visits.19 |
| Patient/Caregiver Experience | Case management has been shown to improve satisfaction and quality of life.20 There is strong evidence that it improves adherence to treatment guidelines and patient satisfaction.21 |
| Social Determinants of Health / Health Related Social Needs/ Health Equity | Community-based case management services significantly improved clients' ability to abstain from drug use, reduced social problems, supported unmet service needs, and improved satisfaction.22 |
23
CM Models Evidence
MGPO CM Program
- 20% reduction in hospital admissions
- 13% reduction in emergency department visits
- 7% annual savings
Health Quality Partners Program
- 25% reduction in hospitalizations
- 28% reduction in emergency department visits
- 21% reduction in average monthly Medicare expenditures
IMPACT Program
- 50% reduction in depressive symptoms
- Reduced total health care costs by $3300 per IMPACT patient
